Distance Matrix Analysis
dm.RdConstruct a distance matrix for a given protein structure.
dm(...) # S3 method for pdb dm(pdb, inds = NULL, grp = TRUE, verbose=TRUE, ...) # S3 method for pdbs dm(pdbs, rm.gaps=FALSE, all.atom=FALSE, aligned.atoms.only=NULL, ...) # S3 method for xyz dm(xyz, grpby = NULL, scut = NULL, mask.lower = TRUE, gc.first=FALSE, ncore=1, ...)
Arguments
| pdb | a |
|---|---|
| inds | atom and xyz coordinate indices obtained from |
| grp | logical, if TRUE atomic distances will be grouped according to their residue membership. See ‘grpby’. |
| verbose | logical, if TRUE possible warnings are printed. |
| pdbs | a ‘pdbs’ object as returned by |
| rm.gaps | logical, if TRUE gapped positions are removed in the returned value. |
| all.atom | logical, if TRUE all-atom coordinates from |
| aligned.atoms.only | logical, if TRUE only equivalent (aligned) atoms are considered.
Only meaningful when |
| xyz | a numeric vector or matrix of Cartesian coordinates. |
| grpby | a vector counting connective duplicated elements that
indicate the elements of |
| scut | a cutoff neighbour value which has the effect of excluding atoms, or groups, that are sequentially within this value. |
| mask.lower | logical, if TRUE the lower matrix elements (i.e. those below the diagonal) are returned as NA. |
| gc.first | logical, if TRUE will call gc() first before calculation of
distance matrix. This is to solve the memory overload problem when |
| ncore | number of CPU cores used to do the calculation.
|
| ... | arguments passed to and from functions. |
Details
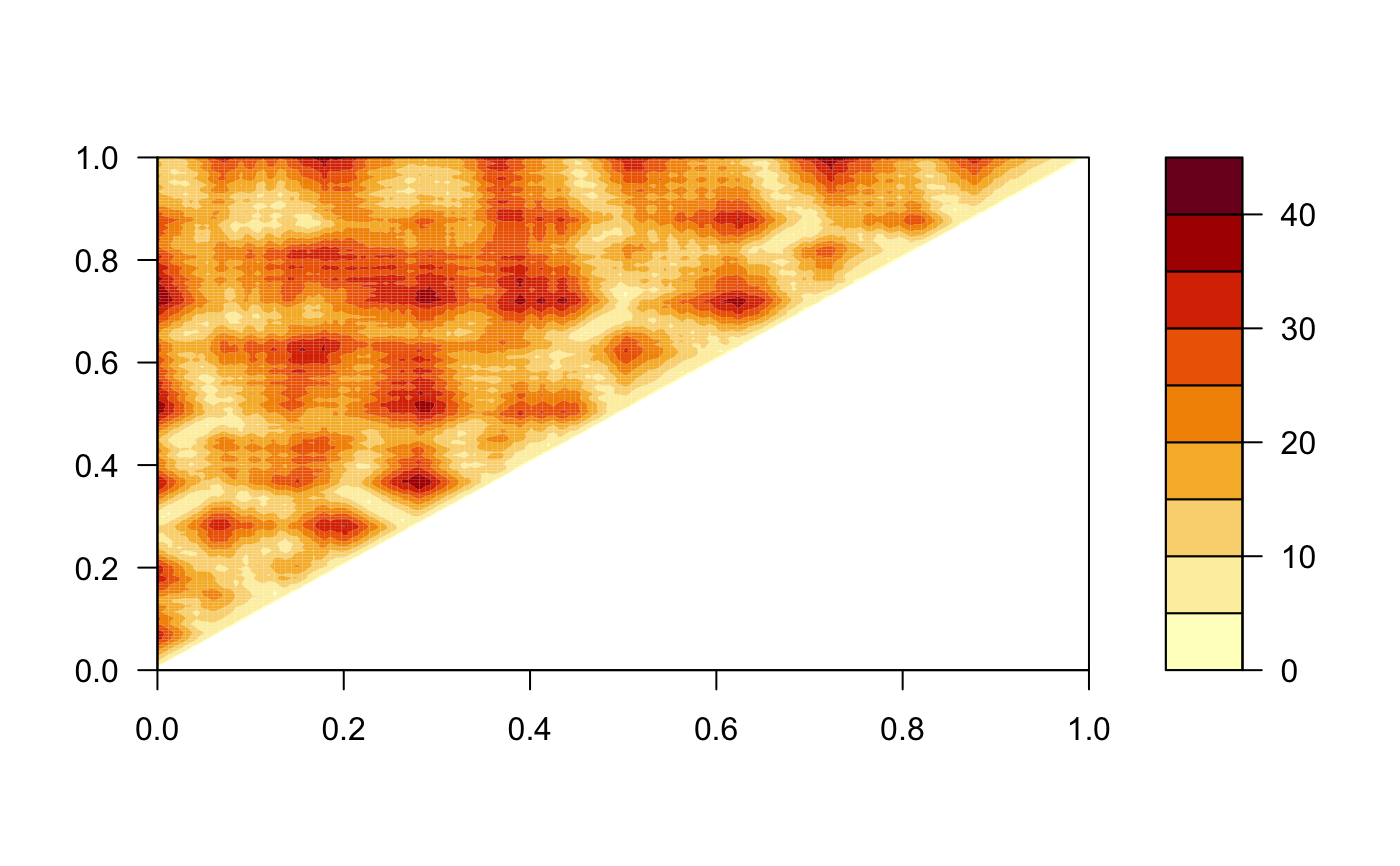
Distance matrices, also called distance plots or distance maps, are an established means of describing and comparing protein conformations (e.g. Phillips, 1970; Holm, 1993).
A distance matrix is a 2D representation of 3D structure that is independent of the coordinate reference frame and, ignoring chirality, contains enough information to reconstruct the 3D Cartesian coordinates (e.g. Havel, 1983).
Value
Returns a numeric matrix of class "dmat", with all N by N
distances, where N is the number of selected atoms. With multiple
frames the output is provided in a three dimensional array.
References
Grant, B.J. et al. (2006) Bioinformatics 22, 2695--2696.
Phillips (1970) Biochem. Soc. Symp. 31, 11--28.
Holm (1993) J. Mol. Biol. 233, 123--138.
Havel (1983) Bull. Math. Biol. 45, 665--720.
Author
Barry Grant
Note
The input selection can be any character string or pattern
interpretable by the function atom.select. For example,
shortcuts "calpha", "back", "all" and selection
strings of the form /segment/chain/residue number/residue
name/element number/element name/; see atom.select
for details.
If a coordinate vector is provided as input (rather than a pdb
object) the selection option is redundant and the input vector
should be pruned instead to include only desired positions.
See also
plot.dmat, read.pdb, atom.select
Examples
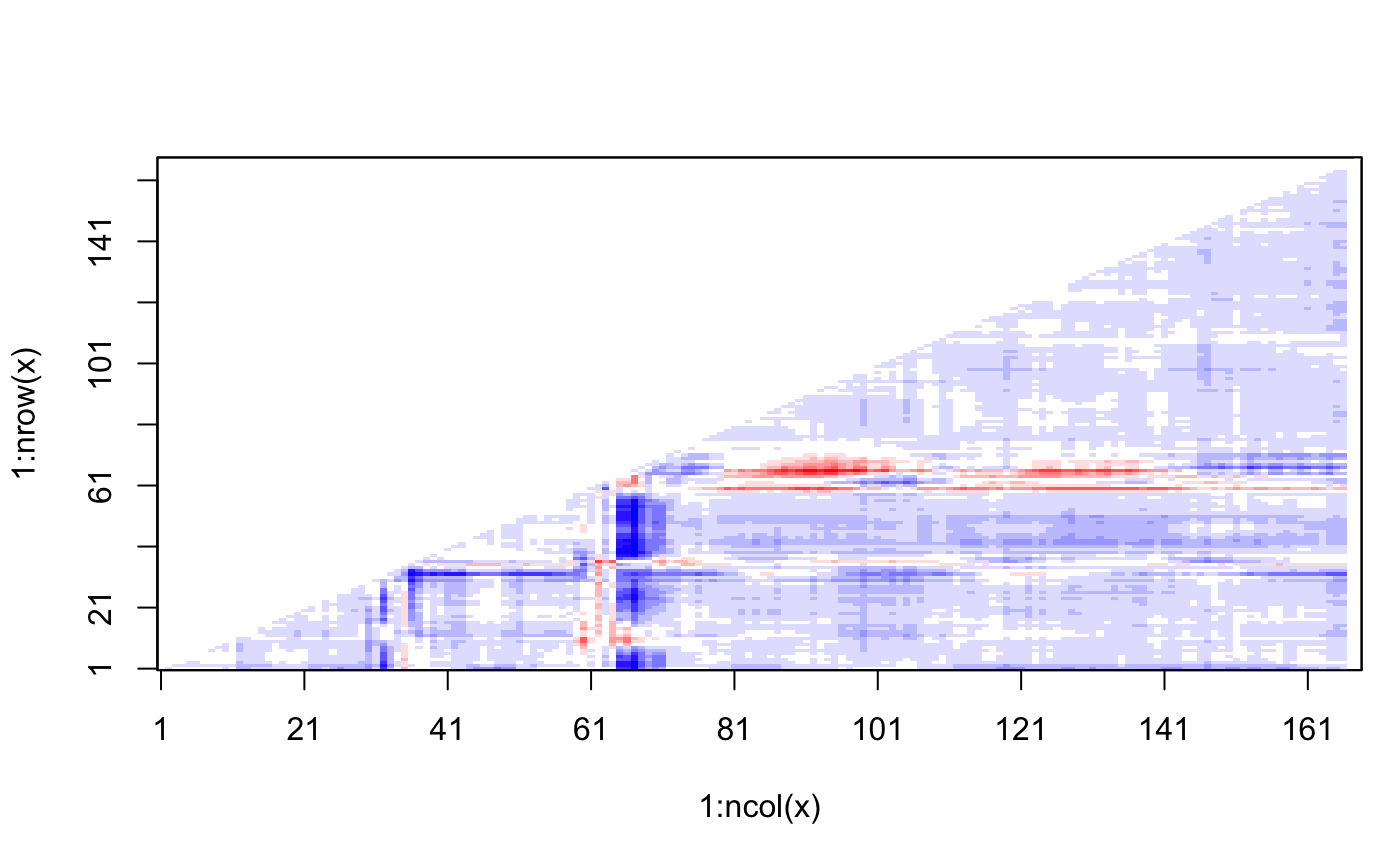
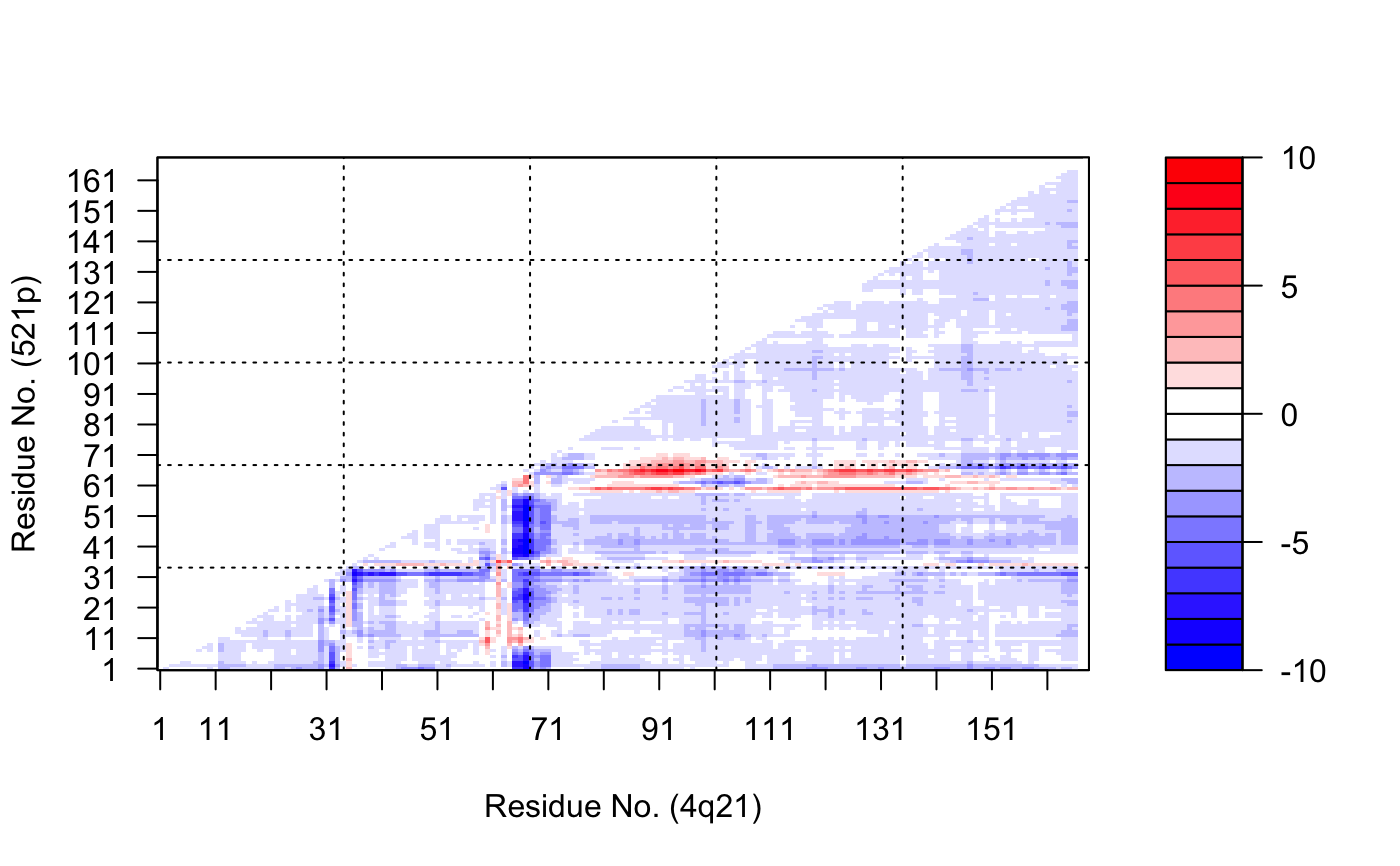
# \donttest{ # PDB server connection required - testing excluded ##--- Distance Matrix Plot pdb <- read.pdb( "4q21" )#> Note: Accessing on-line PDB file#> Warning: /var/folders/xf/qznxnpf91vb1wm4xwgnbt0xr0000gn/T//Rtmp4WslmZ/4q21.pdb exists. Skipping download## NOTE: FOLLOWING EXAMPLE NEEDS MUSCLE INSTALLED if(check.utility("muscle")) { ##--- DDM: Difference Distance Matrix # Downlaod and align two PDB files pdbs <- pdbaln( get.pdb( c( "4q21", "521p"), path = tempdir() ), outfile = tempfile() ) # Get distance matrix a <- dm.xyz(pdbs$xyz[1,]) b <- dm.xyz(pdbs$xyz[2,]) # Calculate DDM c <- a - b # Plot DDM plot(c,key=FALSE, grid=FALSE) plot(c, axis.tick.space=10, resnum.1=pdbs$resno[1,], resnum.2=pdbs$resno[2,], grid.col="black", xlab="Residue No. (4q21)", ylab="Residue No. (521p)") }#> Warning: /var/folders/xf/qznxnpf91vb1wm4xwgnbt0xr0000gn/T//Rtmp4WslmZ/4q21.pdb exists. Skipping download#> Reading PDB files: #> /var/folders/xf/qznxnpf91vb1wm4xwgnbt0xr0000gn/T//Rtmp4WslmZ/4q21.pdb #> /var/folders/xf/qznxnpf91vb1wm4xwgnbt0xr0000gn/T//Rtmp4WslmZ/521p.pdb #> .. #> #> Extracting sequences #> #> pdb/seq: 1 name: /var/folders/xf/qznxnpf91vb1wm4xwgnbt0xr0000gn/T//Rtmp4WslmZ/4q21.pdb #> pdb/seq: 2 name: /var/folders/xf/qznxnpf91vb1wm4xwgnbt0xr0000gn/T//Rtmp4WslmZ/521p.pdb# } if (FALSE) { ##-- Residue-wise distance matrix based on the ## minimal distance between all available atoms l <- dm.xyz(pdb$xyz, grpby=pdb$atom[,"resno"], scut=3) }